charles cordier
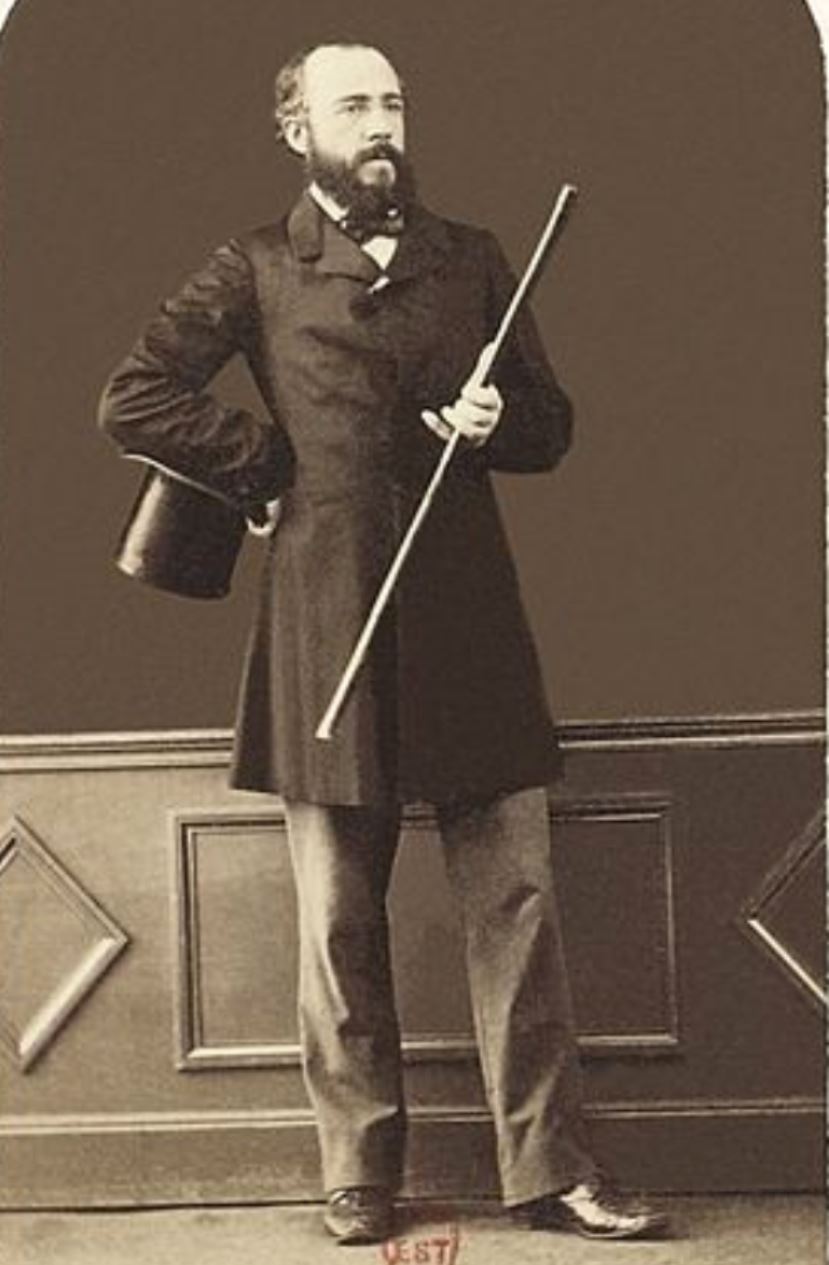

Charles Cordier, full name Charles Henri Joseph Cordier, was a French painter and innovative sculptor.
Charles Cordier studied in Paris at the École des Beaux-Arts and during his studies met a black sitter, a former slave, this meeting and predetermined his future creative life. In 1848, when slavery was officially abolished in all French colonies, Cordier exhibited his first plaster bust of a Sudanese man and received his first success.
For fifteen years, from 1851 to 1866, Cordier was the official sculptor of the Musée National d'Histoire Historique in Paris, creating a series of busts for the ethnographic gallery. Collecting images and types of various ethnic groups, the artist traveled extensively throughout Italy, Greece, Egypt, and Algeria, as well as France itself. Cordier's works are notable for their striking naturalism, and he also made spectacular use of the colors of various materials - marble of different shades, onyx and bronze, silvering and enamel.
Cordier openly defended the advanced for that time the idea of equality of all races. "Each race," he declared, "has its own special type of beauty. The most beautiful black man is not at all the one who looks more like a white man than anyone else."
Cordier also worked on the sculptural decoration of the Paris Opera House, the Louvre, and the Paris Town Hall. His son was the sculptor Henri Louis Cordier.


Charles Cordier, full name Charles Henri Joseph Cordier, was a French painter and innovative sculptor.
Charles Cordier studied in Paris at the École des Beaux-Arts and during his studies met a black sitter, a former slave, this meeting and predetermined his future creative life. In 1848, when slavery was officially abolished in all French colonies, Cordier exhibited his first plaster bust of a Sudanese man and received his first success.
For fifteen years, from 1851 to 1866, Cordier was the official sculptor of the Musée National d'Histoire Historique in Paris, creating a series of busts for the ethnographic gallery. Collecting images and types of various ethnic groups, the artist traveled extensively throughout Italy, Greece, Egypt, and Algeria, as well as France itself. Cordier's works are notable for their striking naturalism, and he also made spectacular use of the colors of various materials - marble of different shades, onyx and bronze, silvering and enamel.
Cordier openly defended the advanced for that time the idea of equality of all races. "Each race," he declared, "has its own special type of beauty. The most beautiful black man is not at all the one who looks more like a white man than anyone else."
Cordier also worked on the sculptural decoration of the Paris Opera House, the Louvre, and the Paris Town Hall. His son was the sculptor Henri Louis Cordier.



Charles Cordier, full name Charles Henri Joseph Cordier, was a French painter and innovative sculptor.
Charles Cordier studied in Paris at the École des Beaux-Arts and during his studies met a black sitter, a former slave, this meeting and predetermined his future creative life. In 1848, when slavery was officially abolished in all French colonies, Cordier exhibited his first plaster bust of a Sudanese man and received his first success.
For fifteen years, from 1851 to 1866, Cordier was the official sculptor of the Musée National d'Histoire Historique in Paris, creating a series of busts for the ethnographic gallery. Collecting images and types of various ethnic groups, the artist traveled extensively throughout Italy, Greece, Egypt, and Algeria, as well as France itself. Cordier's works are notable for their striking naturalism, and he also made spectacular use of the colors of various materials - marble of different shades, onyx and bronze, silvering and enamel.
Cordier openly defended the advanced for that time the idea of equality of all races. "Each race," he declared, "has its own special type of beauty. The most beautiful black man is not at all the one who looks more like a white man than anyone else."
Cordier also worked on the sculptural decoration of the Paris Opera House, the Louvre, and the Paris Town Hall. His son was the sculptor Henri Louis Cordier.
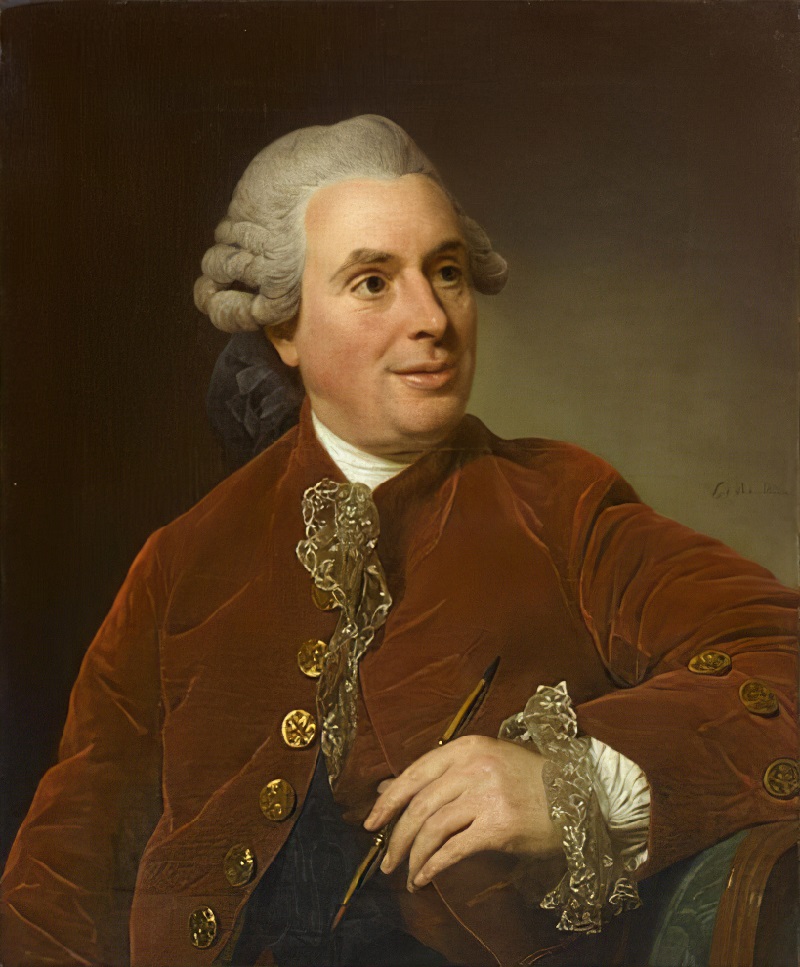


Charles-Nicolas Cochin was a French engraver, designer, writer, and art critic. To distinguish him from his father of the same name, he is variously called Charles-Nicolas Cochin the Younger, Charles-Nicolas Cochin the son, or Charles-Nicolas Cochin II.
More than fifteen hundred works by Cochin can be identified. They include historical subjects, book illustrations, and portraits in pencil and crayon. The richest collection of his engravings, apparently selected by himself, is in the Royal Library, now part of the Bibliothèque nationale.


Girolamo Franzosi was an Italian physician and philosopher.
He was born in Polpenazza (now Polpenazze del Garda), near the Lombard lakeshore, in the late sixteenth and early seventeenth centuries. Franzosi was a student at Padua and became a convinced Aristotelian. He opposed the anatomists of the Neoteric Academy, which represented the new trends of medicine in Verona in contrast to the Galenic tendencies of traditional medicine.
Franzosi's other works, written under the influence of Girolamo Cardano and Agostino Nifo, deal with such wide-ranging topics as dreams, prophecies, imagination, and the medicinal properties of viper venom. He printed most of his works in Verona, calling himself "medicus and philosopher of Verona".









![[QIANLONG, Empereur de Chine (1711-1799) et Charles-Nicolas COCHIN (1715-1790), dir.]](/assets/image/picture_3601309/f9d87/rqfwcmyodhwl6a3u3cnvjqatap9yfxpvbnyt77bbuqb0bh1q4smembav9v5ika1700204263jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[QIANLONG, Empereur de Chine (1711-1799) et Charles-Nicolas COCHIN (1715-1790), dir.]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3601309/f9d87/rqfwcmyodhwl6a3u3cnvjqatap9yfxpvbnyt77bbuqb0bh1q4smembav9v5ika1700204263jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)